Load Cell Calibration
January 27, 2021
Before any load cell can be used it must undergo an initial load cell calibration. The purpose is to convert the output voltage to a user-defined value. In other words, the data processing components of the system have to be taught how to convert mV/V from the load cell to a force measurement value.
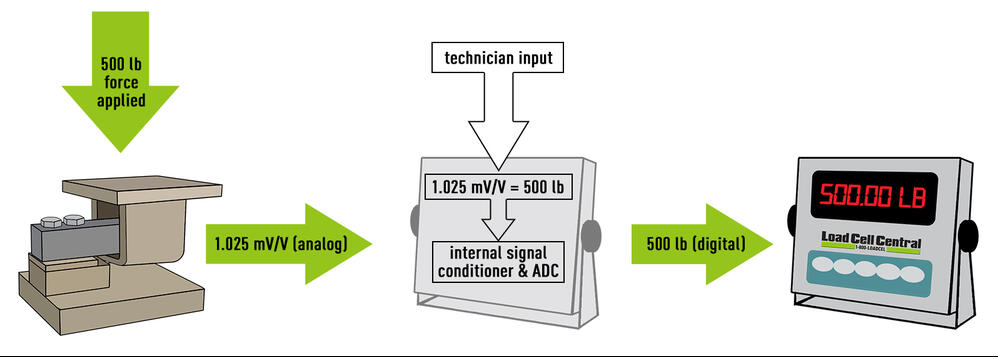
Future calibrations can also be compared to the initial calibration data to determine if there are structural or electrical issues with the load cell.
Recalibrating your Load Cell
Age, use, overloading, off-axis loading, harsh environmental conditions, and numerous other factors can affect a load cell’s performance over time. This is why it is important to recalibrate a load cell at regular intervals. It is typically required that load cells be recalibrated every year, ideally using the same digital indicator and other components included in the system application. Load cells that experience continuous use or are used in harsh environments will likely require more frequent calibration.
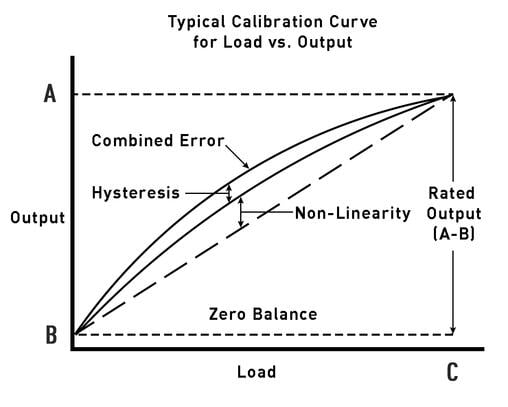
Load Cell Calibration Accuracy
During calibration, the accuracy of a load cell is determined by testing repeatability and linearity. The standard calibration method requires a set of 5 known loads to be applied to the load cell, with output measurements taken at each load. For example, a 10K lb load cell would have output measured at 2K, 4K, 6K, 8K, and 10K lbs. The data from these measurements is used to determine the accuracy of the load cell. The accuracy of a load cell is expressed in terms of 1) Non-linearity 2) Hysteresis and 3) Combined Error. See graph below.